Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg has declared that "we believe Meta AI is now the smartest AI assistant you can freely use." On April 19, Meta officially announced the release of the next generation of its state-of-the-art open-source large language model—Llama 3. Trained on a 24K GPU cluster with 15T of data, Llama 3 offers pre-trained and instruction-tuned versions with 8 billion and 70 billion parameters.
Performance Rivaling GPT-4
Notably, Llama 3's performance has been significantly enhanced through improvements in post-training procedures, which have reduced error rejection rates, improved alignment, and increased the diversity of model responses. Meta's research team has also observed substantial improvements in reasoning, code generation, and instruction following capabilities, making Llama 3 more controllable.
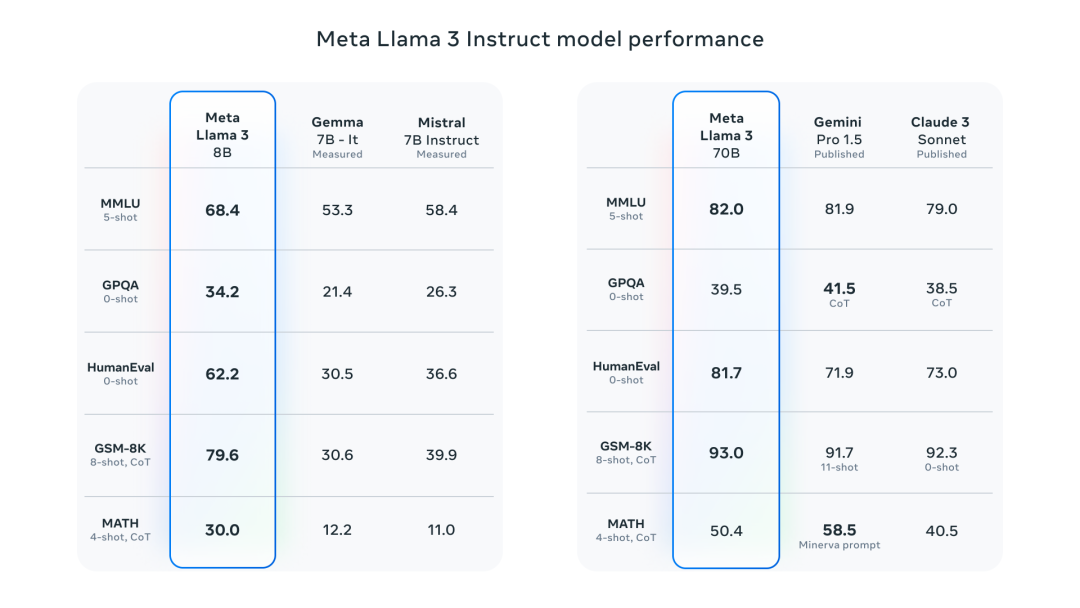
The 8 billion parameter model outperforms models like Gemma 7B and Mistral 7B Instruct on multiple benchmarks, including MMLU, GPQA, and HumanEval. The 70 billion parameter model surpasses the closed-source superstar model Claude 3 Sonnet and is on par with Google's Gemini Pro 1.5 in performance.
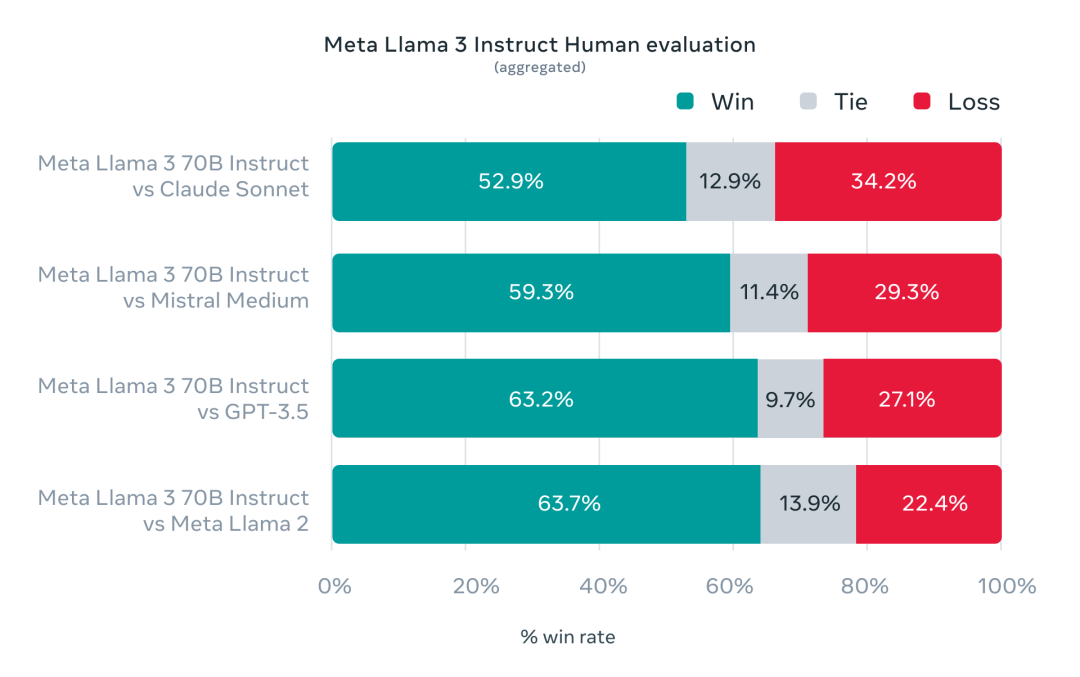
Meta has also tested Llama 3 in real-world scenarios by developing a new high-quality human evaluation set comprising 1,800 prompts covering 12 key use cases (such as soliciting advice, brainstorming, categorization, answering closed-ended questions, coding, creative writing, extraction, role/character portrayal, answering open-ended questions, reasoning, paraphrasing, and summarization). Compared to Claude Sonnet, Mistral Medium, and GPT-3.5, Llama 3 shows superior performance.
Key Features of Llama 3
Meta aims to make the most powerful Llama 3 models multimodal, enabling them to receive text, images, and even videos as input and generate outputs in these diverse formats. These models will also support multiple languages and have a larger "context window," allowing them to process large volumes of data for analysis or summarization. This larger context window has been shown to reduce the model's hallucination rate, or the frequency at which the model outputs inaccurate information in response to prompts. Additionally, Llama 3 boasts improved reasoning and coding capabilities.
Meta is currently training a version of Llama 3 with over 400 billion parameters, which is set to outperform Claude 3.
The Four Key Elements Behind Llama 3's Success
Meta attributes Llama 3's strength as the most powerful open-source large language model to four key factors: model architecture, pre-training data, scaling pre-training, and instruction tuning.
Model Architecture: Llama 3 uses a relatively standard pure-decoder Transformer architecture with several key improvements over Llama 2. It employs a 128K token tokenizer that more efficiently encodes language, significantly boosting model performance. For enhanced inference efficiency, Meta implemented grouped query attention (GQA) in the 8 billion and 70 billion parameter models. The models were trained on sequences of up to 8,192 tokens with masks to prevent cross-document boundary attention.
Pre-Training Data: Meta emphasizes that the key to training the best language model is curating a large, high-quality training dataset. Llama 3 was pre-trained on over 15T tokens, seven times the dataset size of Llama 2 and containing four times the amount of code. The pre-training dataset includes over 5% high-quality non-English data covering more than 30 languages. To ensure high-quality training data, Meta developed a series of data filtering pipelines, including heuristic filters, NSFW filters, semantic deduplication methods, and text classifiers to predict data quality. They also conducted extensive experiments to determine the optimal method for mixing data from different sources in the final pre-training dataset.
Scaling Pre-Training: To effectively utilize pre-training data in the Llama 3 models, Meta developed detailed scaling laws for downstream benchmark evaluation. These laws enabled them to select the best data combinations and make optimal decisions on training computation usage. Importantly, scaling laws allowed Meta to predict the performance of the largest models on key tasks (such as code generation on the HumanEval benchmark) before actual training. This contributed to Llama 3's strong performance across various use cases and functionalities. During Llama 3's development, Meta observed new scaling behaviors. For instance, although the optimal training computation for the 8 billion parameter Chinchilla model is equivalent to 200B tokens, they found that performance continues to improve even after training on data two orders of magnitude larger. The 8 billion and 70 billion parameter Llama 3 models showed logarithmic linear growth in performance even after training on up to 15T tokens.
Instruction Tuning: To fully unleash the potential of the pre-trained model in chat use cases, Meta innovated its instruction tuning methods. Their post-training approach combines supervised fine-tuning (SFT), rejection sampling, approximate policy optimization (PPO), and direct policy optimization (DPO). The quality of prompts used in SFT and preferences used in PPO and DPO significantly impacts model performance. Learning preferences through PPO and DPO also greatly enhanced Llama 3's performance in reasoning and coding tasks. They found that if the model is presented with a reasoning question it struggles to answer, it sometimes generates the correct reasoning trajectory: the model knows how to arrive at the correct answer but doesn't know how to select it. Training on preferences teaches the model how to choose the correct answer.
Availability and Future Plans
Both the base and Instruct versions of Llama 3 with two parameter sizes are now available on Hugging Face for download. Additionally, cloud service platforms such as Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Amazon AWS, and NVIDIA NIM will also roll out Llama 3 in the near future. Meta also announced that Llama 3 will be supported by hardware platforms from Intel, NVIDIA, AMD, and Qualcomm.
Meta's Vision for AIGC
Since Meta first launched the free Llama series of models, they have been among the most popular open-source models on the market. With the introduction of Llama 3, the landscape of generative AI has changed significantly. However, Meta faces increasing competition from other open-source contenders and companies offering paid closed-access models. The release of these new models represents Meta's attempt to match some of the features provided by competitors like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google in their latest models, which have so far only been available in closed, paid proprietary services.
As many industry observers expected, Meta initially released two smaller versions of Llama 3, stating in a press release that "this is the best open-source model of its kind" and that it will soon be available on AWS, Google Cloud, Databricks, Microsoft Azure, and Hugging Face. However, these models do not match the capabilities of some of the highest-performing proprietary models on the market.
The larger version of Llama 3 (with over 400 billion parameters) is currently in training, and the company plans to decide whether and how to release it after several months of safety testing.
The Battle for AI Talent
The competition for AI talent continues to heat up, with top researchers and many former big-tech engineers jumping ship to start their own startups. Meta has recently experienced its own AI talent drain, including the departure of several senior executives, including the head of generative AI. This has had an impact on Zuckerberg's ongoing generative AI race: if Meta wants to stay ahead, it needs to ensure it can retain the top AI talent qualified to build these models. Conversely, building the best models helps attract top talent, who are usually drawn to the most ambitious AI labs.
AI as Meta's Top Priority
AI has become Meta's top priority, replacing the company's previous emphasis on the metaverse. In October last year, Zuckerberg stated, "AI will be our biggest investment area in 2024, both in engineering and computing resources." As part of today's Llama announcement, he doubled down on this theme, stating, "We are making significant investments to build leading AI."
Meta is also a long-time advocate of open-source research. It has created an open-source ecosystem around the PyTorch framework and recently celebrated the 10th anniversary of FAIR (Fundamental AI Research), which was established to "advance the state of AI through open research for the benefit of all" and has been led by Meta's Chief Scientist Yann LeCun.
LeCun pushed for the commercial license release of Llama 2 and model weights. "I advocated for this internally," he said at the AI Native conference in September 2023. "I believe it is inevitable because large language models will become infrastructure that everyone uses, and it must be open."
Meta Vice President of AI Mahohar Paluri told Fortune that the current fierce competition in open-source AI makes the company feel "our mission to accelerate innovation and innovate openly is supported and validated, so that we can build safer and more efficient models." Each iteration will become better and better. The more models built on top of each other, including Llama, "the faster we make progress in delivering more use cases to end users."